Animals and plants are both living organisms with many similarities. However, there are some important differences between animal and plant cells. Eukaryotic cells, like animal and plant cells, have a nucleus, organelles, and a membrane-bound structure. Despite their similarities, there are several structural and functional differences between animal and plant cells. Let us understand more about the comparison between plant cells and animal cells.
To understand deeply the difference between animal and plant cells, it is best to understand their definition or essentials.
What is an Animal Cell?
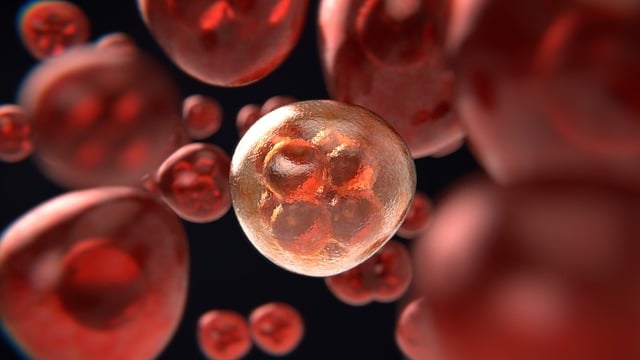
An animal cell is a type of eukaryotic cell found in all multicellular organisms that controls the organism’s structure and function. A nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, lysosomes, centrioles, and other structures and organelles are all found in animal cells. Because it contains the genetic material, the nucleus is the most important organelle in the cell. A membrane surrounds the nucleus, which protects the genetic material and regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the nucleus. The mitochondria are the cell’s power producers, responsible for generating energy.
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that aids in the production of proteins and other molecules. Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis and can be found in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Lysosomes are in charge of disassembling and recycling cellular components. Centrioles are microtubules found in the cytoplasm of cells. A cell membrane, cytoplasm, and a cytoskeleton are also found in animal cells.
The cell membrane is responsible for controlling what enters and exits the cell. The cytoplasm, a gel-like substance, houses the organelles and other structures. The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that aids in cell shape and structure. It also helps the cell move, divide, and perform other functions. In summary, an animal cell is a type of eukaryotic cell that is in charge of the organism’s structure and function. It has a nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, lysosomes, centrioles, cell membrane, cytoplasm, and cytoskeleton, among other organelles and structures. Each of these elements is necessary for proper cell function.
What is a plant cell?
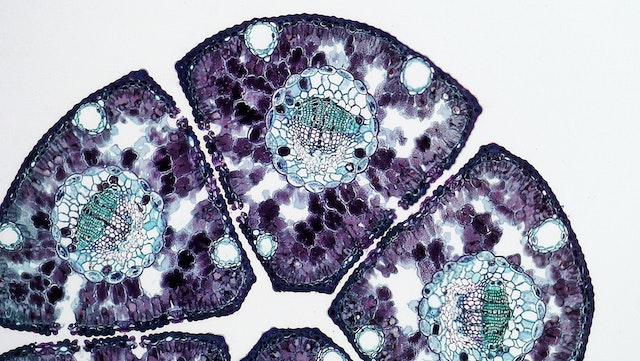
Plant cells are the most common type of cell found in Plantae organisms. Plant cells are eukaryotic, meaning they have a nucleus and other cellular structures surrounded by a membrane. Plant cells differ from eukaryotic cells found in animals and fungi. One of the most well-known characteristics of plant cells is the presence of a cell wall. This cellulose-based cell wall protects and structures the cell while also preventing it from bursting due to osmotic pressure changes. Because of this cell wall, plant cells have a rectangular shape. Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that are required for photosynthesis, which is the process by which light energy is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use for energy.
Also Read > Difference Between Turtle and Tortoise
Chloroplasts are composed of chlorophyll, which is a green pigment found in plants. Large central vacuoles, which are membrane-bound organelles that store water and other molecules while also providing structure to the cell, are also found in plant cells. Vacuoles can also be used to store waste and toxins and to control cell pressure. Plant cells also have mitochondria, which are energy-producing organelles. Mitochondria play an important role in plant growth and development by participating in cell signaling and other processes. Finally, plant cells have organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, and ribosomes.
These organelles are in charge of many processes, including protein synthesis, energy production, and other cellular functions. A cell wall, chloroplasts, large central vacuoles, mitochondria, and various other organelles are all found in plant cells. Plant growth and development require these structures because they provide the structure and energy that plants require to survive.
Animal Vs Plant Cell
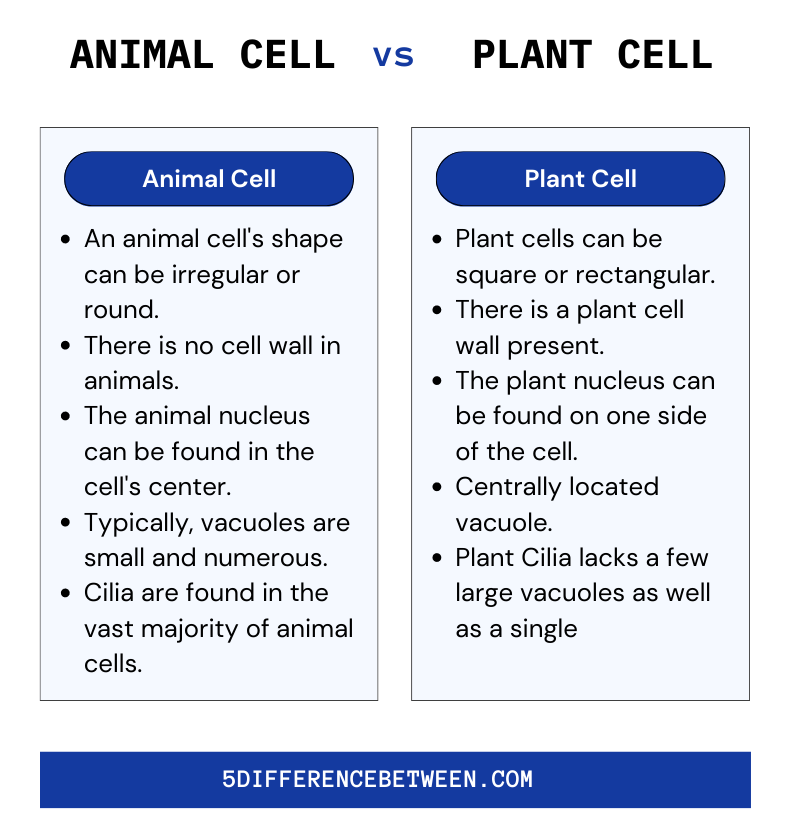
The membrane-bound organelles found in both plant and animal cells include the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, the nucleus, the Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. Plant cells are larger than animal cells. An animal cell’s normal range is 10 – 30 micrometers, while a plant cell’s normal range is 10 – 100 micrometers.





2 Comments to “5 Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell”