Microeconomics focuses on individuals and businesses, while macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a whole. Below this, there are a few key difference micro and macro economics to understand.
Micro Economics: Focused on Individual Markets and Prices
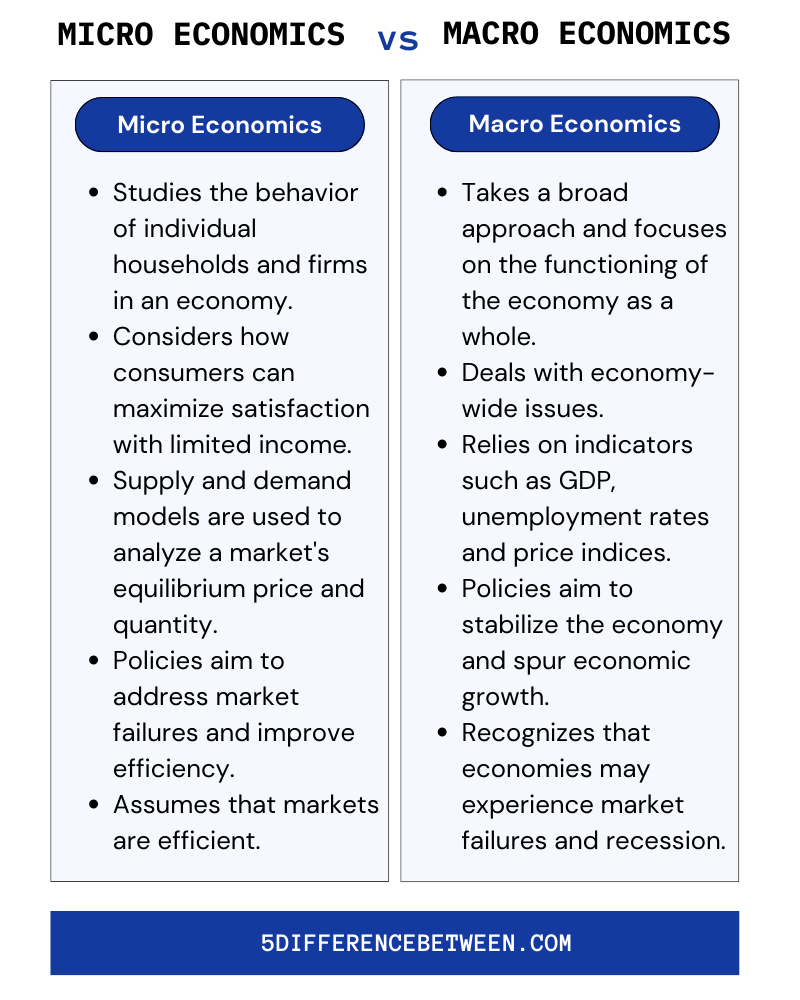
Microeconomics focuses on the behavior of individuals and firms in the economy. It looks at how supply and demand determine prices and how prices determine the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Also Read > Difference Between Sales and Marketing
As an individual in the economy, microeconomics helps you understand how your decisions impact your finances. Things like how much of your budget to spend on rent, how much to save for retirement, or whether it’s worth returning to school. Microeconomics can help calculate the costs and benefits to make the best choice for your situation.
For businesses, microeconomics is crucial for success. It helps determine how much of a good or service to supply based on the demand from consumers like you. If demand goes up, companies may increase supply. If it goes down, they may cut supply to avoid surpluses. Microeconomics also helps set the prices of goods, services, and wages. Prices that are too high can reduce demand, while prices too low may not generate a profit.
Understanding microeconomics gives you and your businesses the power to make prudent decisions based on the factors that directly impact you. While macroeconomics looks at the economy as a whole, microeconomics provides focused insights into how individuals, households and firms behave in the marketplace. They’re two sides of the same coin working together to drive progress.
Macro Economics: Analyzing the Economy as a Whole
Macroeconomics looks at the economy as a whole and focuses on factors like inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. Unlike microeconomics which examines the behavior of individuals and firms, macroeconomics analyzes the economy on an aggregate level.
Some of the major areas of study in macroeconomics include:
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): This measures the total value of all goods and services produced in a country. GDP is actually one of the primary indicators used to gauge the health of a country’s economy.
Unemployment refers to the number of people in an economy who are out of work but actively seeking employment. High unemployment is undesirable as it represents an economy that is not utilizing its resources efficiently.
Inflation: This refers to a general increase in the prices of goods and services over a while. Moderate inflation is okay, but high inflation reduces the purchasing power of money and can negatively impact economic growth.
Economic Growth: This refers to an increase in a nation’s productive capacity and output. Steady economic growth is important for raising living standards and prosperity. Technological improvements, capital investment, and increased labor skills drive growth.
Macroeconomics helps governments, businesses, and individuals make better decisions by providing an overview of where the economy stands and where it may be heading. Understanding these fundamental economic concepts can help us navigate the ups and downs of the global economy.
Micro Vs Macro Economics
In summary, micro and macroeconomics take different approaches but provide a complete view of how economic systems function. Understanding the key differences between the two fields is crucial to comprehensively understanding economics.






