The post 5 Difference Between Open and Closed Mitosis appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>Defining Open and Closed Mitosis
Open Mitosis
In open mitosis, the nuclear envelope breaks down completely during cell division. This means the DNA is exposed to the cytoplasm during mitosis. The nuclear envelope reforms at the end of mitosis around each set of separated DNA. Most animal cells, including human cells, undergo open mitosis.
Closed Mitosis
In closed mitosis, the nuclear envelope remains intact during cell division. The mitotic spindle forms inside the nucleus and chromosomes divide and separate while remaining inside the nuclear envelope. At the end of mitosis, the nuclear envelope is divided between the two new nuclei. Most plant cells and some unicellular eukaryotes like yeasts undergo closed mitosis.
Also Read > Difference Between Cemetery and Graveyard
So in short, Open mitosis involves the breakdown of the nuclear envelope, exposing the DNA. Closed mitosis retains the intact nuclear envelope. The mitotic spindle forms inside the nucleus in closed mitosis but in the cytoplasm in open mitosis. Chromosomes remain within the nucleus at some stage in closed mitosis but circulate into the cytoplasm at some point in open mitosis.
Understanding the meaning of these two types of mitosis enables in perception of how cells divide and propagate in exceptional sorts of organisms. Even as the give-up result—two daughter cells—is equal, the specific mechanisms that get them there can fluctuate. But in all cases, mitosis lets cells divide and provide new cells to support growth, repair damage, and update vintage cells.
When Does Open vs Closed Mitosis Occur?
When cells divide, they go through the method of mitosis. There are two types of mitosis: open and closed. The difference among those types comes down to whether the nuclear envelope stays intact or breaks down.
Open Mitosis
In open mitosis, the atomic envelope encompassing the cell core separates, uncovering the DNA in the core. This endorses the mitotic spindle fibres to get the right section of the DNA and separate the chromosomes. Open mitosis typically occurs in animals and some unicellular organisms.
The breakdown of the nuclear envelope is a basic step since it offers a chance for the mitotic spindle to set up the DNA. The spindle fibres connect to the centromeres of the chromosomes and adjust them at the centre of the cell. Then, the sister chromatids separate and circulate to the opposite ends of the cell. A new nuclear envelope forms around each set of separated DNA, creating two distinct nuclei.
Closed Mitosis
In contrast, closed mitosis retains the nuclear envelope throughout cell division. The mitotic spindle forms inside the nucleus and attaches to the chromosomes, separating the sister chromatids without breaking down the envelope. Closed mitosis primarily occurs in plants, algae, and fungi.
Maintaining the nuclear envelope requires the mitotic spindle to gain access to the DNA through tiny pores in the envelope. The spindle fibres extend through the pores to grab hold of the chromosomes and direct them to opposite ends of the cell. The intact nuclear envelope then simply pinches in two, separating around the midline of the cell to form two new nuclei.
While open and closed mitosis achieves the same end result of genetically identical nuclei, the specific steps involved differ significantly based on whether the nuclear envelope remains intact or breaks down. Understanding these differences provides insight into how diverse life forms have evolved distinct but effective cellular processes.
Open Mitosis Vs Closed Mitosis
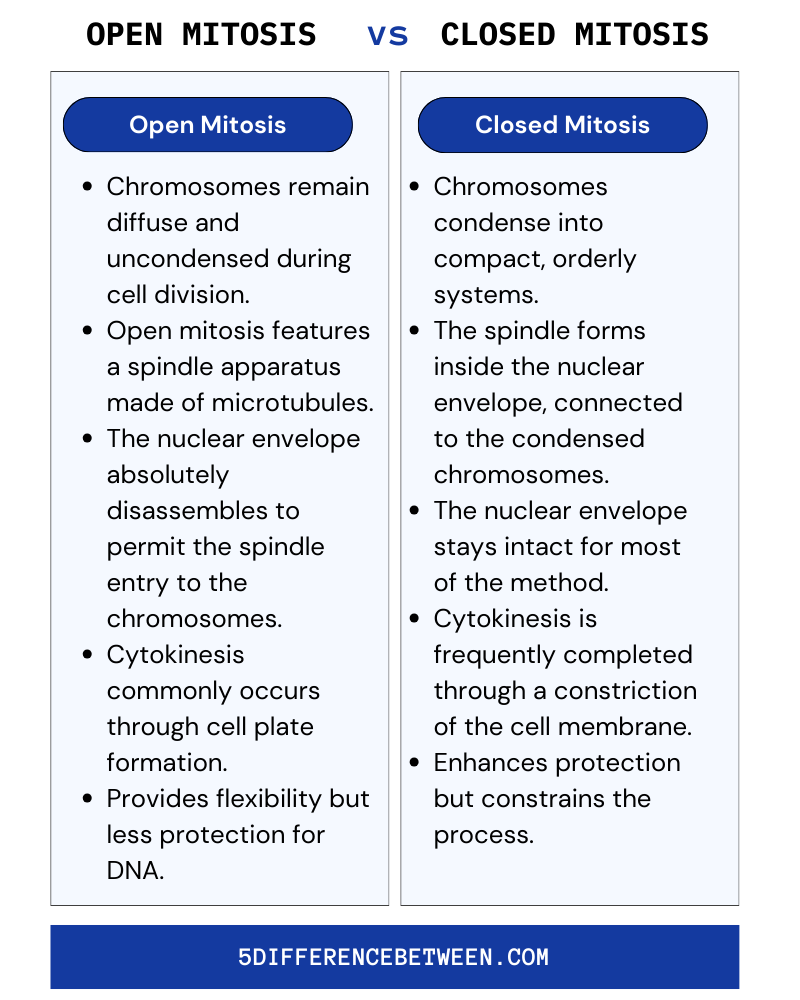
Open Mitosis
- In open mitosis, chromosomes remain diffuse and uncondensed during cell division.
- Open mitosis features a spindle apparatus made of microtubules.
- In open mitosis, the nuclear envelope absolutely disassembles to permit the spindle entry to the chromosomes.
- In open mitosis, cytokinesis commonly occurs through cell plate formation.
- Open mitosis provides flexibility but less protection for DNA.
Closed Mitosis
- In closed mitosis, chromosomes condense into compact, orderly systems to facilitate their separation.
- In closed mitosis, the spindle forms inside the nuclear envelope, connected to the condensed chromosomes.
- In closed mitosis, the nuclear envelope stays intact for most of the method.
- In closed mitosis, cytokinesis is frequently completed through a constriction of the cell membrane, pinching the cell in two.
- Closed mitosis enhances protection but constrains the process.
Knowing the differences between these two types of nuclear departments offers insight into how evolution has formed biology to health the wishes of every organism. Both open and closed mitosis accomplish the essential and complex venture of passing genetic information to the following generation, the very foundation of existence itself.
The post 5 Difference Between Open and Closed Mitosis appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>The post 5 Difference Between Geology and Geomorphology appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>Defining Geology and Geomorphology
Geology
Geology plans to grasp what lies underneath the Earth and how it works. Geologists concentrate on rocks, minerals, and fossils to choose the materials and powers that shape the planet. They concentrate on plate tectonics, earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountains working to get a handle on land processes. Geologists additionally study the beginning and evolution of the Earth and nearby solar system. Generally, geology tries to unravel the secrets of our dynamic Earth.
Geomorphology
Geomorphology, then again, specifically looks at the Earth’s surface and the natural cycles that shape landscapes and landforms. Geomorphologists study erosion, weathering, glaciation, rivers, wind, and tides to comprehend how they slowly yet constantly change the layer of the Earth. They study how elements like climate, rock type, vegetation, and human action impact the advancement of landforms like valleys, beaches, dunes and deltas. Geomorphology expects to understand the reason why the layer of the Earth looks the way it does today.
Also Read > Difference Between Tortilla and Chapati
While geology and geomorphology have distinct focuses, they are complementary and interconnected disciplines. What happens underneath the surface, which geology looks at, eventually decides the landforms we see at the surface, which geomorphology studies. To completely understand our Earth, we want both geology and geomorphology.
Examples of Geology and Geomorphology in Real Life
For example, think about the last time you visited the ocean side. The sand, shells, and stones under your feet are geological materials that have been shipped and kept by geomorphological processes like erosion and sedimentation. The shape and slope of the ocean side itself is a landform made by the communication of geology and geomorphology.
Have you seen any interesting stone developments in your area? The appearance and position of not entirely settled by geographical variables like mineral composition and geomorphological factors, for example, weathering and erosion from wind and water. Huge stone cliffs, arches, and pillars are etched over time through the gradual breakdown and removal of rock.
Rivers, streams, and canyons additionally showcase geology and geomorphology cooperating. As water flows over and through rock and soil, it dissolves the land, diverting sediment and carving valleys and channels. The particular way a river takes relies upon the local geology and how effectively the material can be dissolved. Wandering rivers bend and twist, and while rivers flow on both sides, the safe stone will more often than not be straighter.
Indeed, even earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and sinkholes are signs of geology and geomorphology in real life. The unexpected movements of Earth’s plates during earthquakes alter the scene, while volcanoes fabricate mountains and reshape the surface. Sinkholes structure when surface material erodes or breaks up away to uncover openings in the bedrock beneath.
The natural world around us is perpetually captivating. Understanding geology and geomorphology makes sense of how the layer of our planet came to seem the manner in which it does today. Each stone, river, and landform has a story to tell.
Geology vs Geomorphology
Geology and geomorphology are connected however distinct fields of study. The following are five of the main distinctions between them:
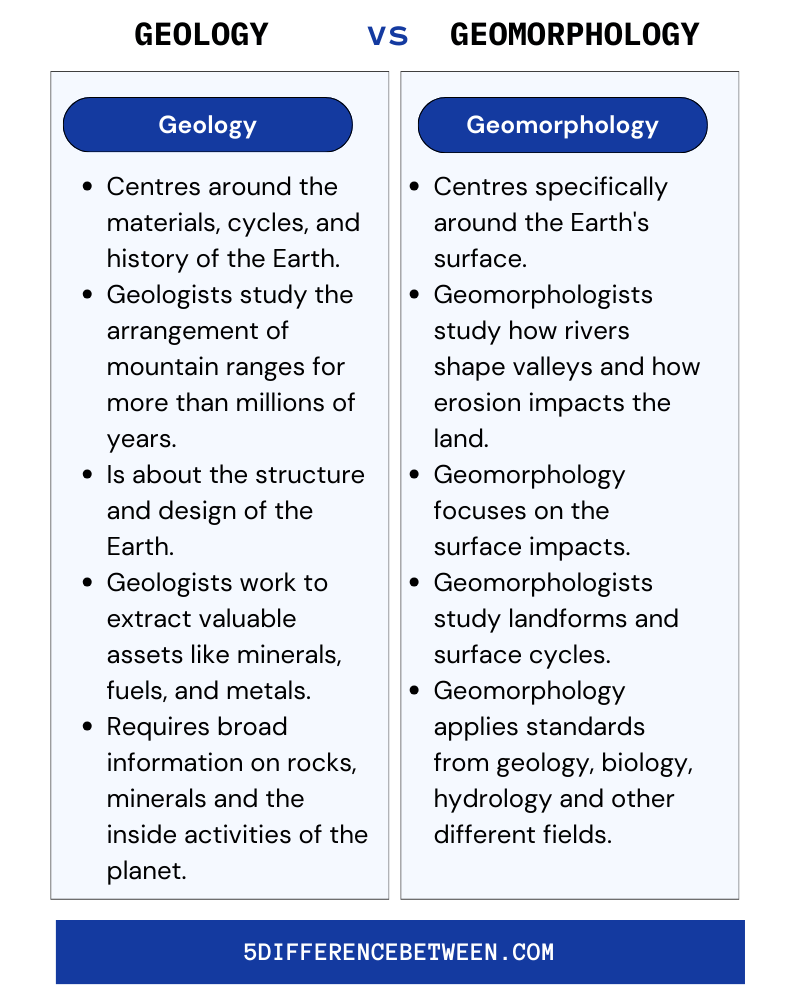
Geology
- Geology centres around the materials, cycles, and history of the Earth.
- Geologists might have studied the arrangement of mountain ranges for more than millions of years.
- Geology is more worried about the structure and design of the Earth, including plate tectonics and the stone cycle.
- Geologists frequently work to find and extract valuable assets like minerals, fuels, and metals.
- Geology requires broad information on rocks, minerals and the inside activities of the planet.
Geomorphology
- Geomorphology centres specifically around the Earth’s surface highlights and how they structure and change after some time.
- Geomorphologists take a look at what rivers shape valleys and how erosion impacts the land over hundreds of years or less.
- Geomorphology focuses on the surface impacts of these cycles, for example, how tectonic powers make landforms like faults, folds and volcanoes.
- Geomorphologists study landforms and surface cycles to assist with land management, hazard mitigation, and protection.
- Geomorphology applies standards from geology, biology, hydrology and different fields to comprehend how the Earth’s surface is formed by wind, water, ice and different specialists.
In summary, while geology and geomorphology are firmly related disciplines, they vary in their extension, timescales of study, topic, applications, and interdisciplinary nature. Both give important experiences into the activities of our dynamic planet.
The post 5 Difference Between Geology and Geomorphology appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>The post 5 Difference Between Stream And Brook appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>Defining a Stream: Size, Flow Rate, and Features
A stream is a small watercourse that flows through a channel with defined banks. Streams are normally smaller than rivers and creeks. The water in a stream flows at a mild price, permitting a few sediments to settle into the stream bed.
The scale and flow rate of a stream can vary greatly depending on factors like:
- Season – Streams often swell in size during rainy seasons or spring snowmelt and shrink during drier summer months or winter freezes.
- Watershed – The land area that drains into a stream impacts how much water flows through it. Larger watersheds mean more water is collected and carried to the stream.
- Gradient – How steep the stream bed is will affect how fast the water flows. Steeper gradients lead to faster flow rates as the water rushes downhill.
Also Read > Difference Between Wallpaper and Screensaver
Some common features you’ll find in streams include:
- Riffles – Shallow, fast-flowing sections where the water bubbles over rocks.
- Pools – Deeper, slower-moving sections where fine sediment and debris collect.
- Meanders – Winding curves in the stream channel. As streams flow over land, they erode sediment and meander.
- Floodplains – Flat areas along the stream banks that become submerged when the stream overflows its banks.
- Deltas – Fan-molded deposits that structure when streams empty into huge waterways like lakes or seas. The slowing water loses its capacity to convey dregs, losing it on the stream mouth.
Defining a Brook: Size, Flow Rate, and Features
A brook is a small stream, typically narrow and shallow, often winding through woods or fields. Brooks are usually smaller than creeks, with a slower flow rate and calmer waters. The word “brook” conjures up pics of a quiet, mild body of water, best for skipping stones or sitting at the same time as enjoying the sounds of nature.
Brooks are normally not quite a few feet wide and a foot or two deep at most. They have a leisurely flow rate since their watersheds, the land area that drains into them, are small. The water in a brook is frequently clean since it moves slowly ample for heavier sediments to settle out. You can spot small fish darting about and frogs lounging at the banks of a brook.
Some characteristics of brooks include:
- Meandering path: Brooks frequently curve and bend as they flow over the land. Their slow-moving waters are effortlessly diverted around barriers and comply with the course of least resistance.
- Rocky or gravel bed: The bottom of a brook commonly includes small rocks, gravel, and sand that the flowing water has shaped and smoothed over time.
- Vegetated banks: Brooks typically have grassy or forested banks with plant life, shrubs and trees growing properly as much as the water’s aspect. The plant life presents colouration and habitat for wildlife.
- Riffles and pools: Brooks frequently change between shallow, fast-moving sections (riffles) and deeper, slower pools alongside their path. Riffles upload oxygen to the water at the same time as pools provide habitat for fish and different aquatic animals.
- Seasonal flow changes: The flow rate of a brook has a tendency to range all through the year, growing in the spring and winter rainy seasons, and decreasing within the summertime and fall. Some brooks may additionally even dry up completely for the duration of drought durations, though their streambeds stay in the vicinity till the following rains.
The babbling waters and herbal surroundings surrounding a brook create an idyllic setting for relaxation and recreation. No wonder Brooks has inspired so many poets and artists over the centuries!
Stream vs Brook
A stream and a brook are both flowing bodies of freshwater, however, there are a few key variations between the two. Let’s explore how they vary.
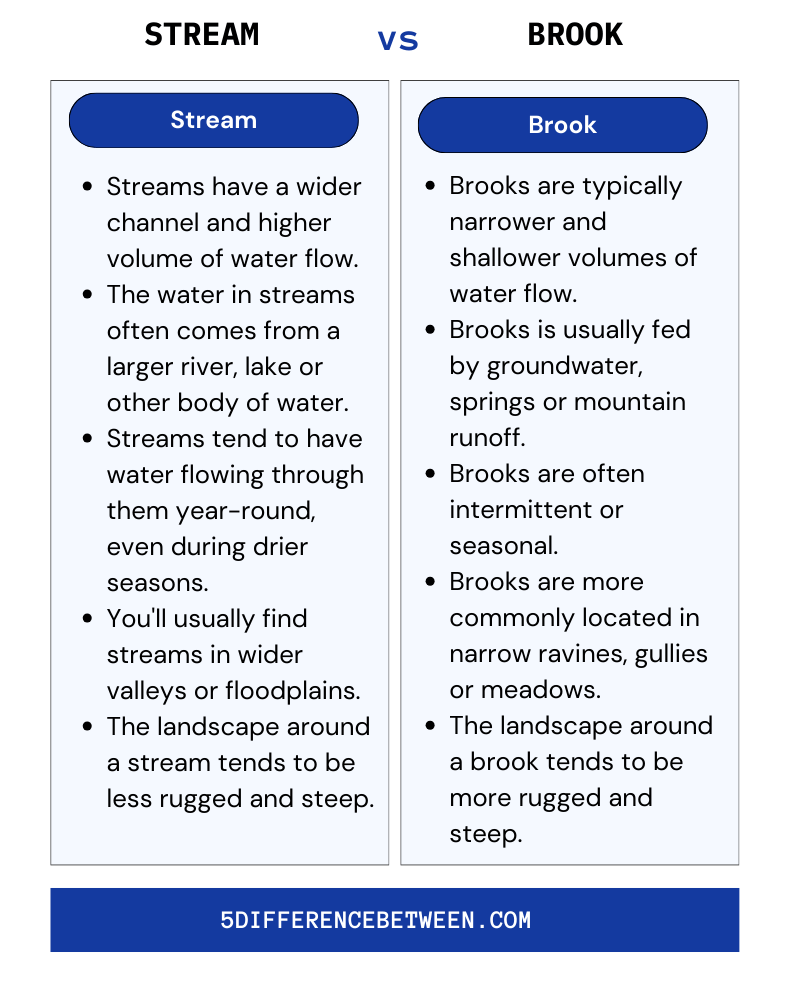
Stream
- Streams have a wider channel and higher volume of water flow.
- The water in streams often comes from a larger river, lake or other body of water.
- Streams tend to have water flowing through them year-round, even during drier seasons.
- You’ll usually find streams in wider valleys or floodplains.
- The landscape around a stream tends to be less rugged and steep.
Brook
- Brooks are typically narrower and shallower volumes of water flow.
- Brooks is usually fed by groundwater, springs or mountain runoff.
- Brooks are often intermittent or seasonal, drying up during parts of the year when there is little rainfall.
- Brooks are more commonly located in narrow ravines, gullies or meadows.
- The landscape around a brook tends to be more rugged and steep.
In summary, while streams and brooks are both flowing freshwater courses, streams are generally larger, faster, more permanent and found in wider landscapes than their smaller brook counterparts. But no matter the differences, both provide habitat for wildlife and scenic natural beauty.
The post 5 Difference Between Stream And Brook appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>The post 5 Difference Between Holly and Mistletoe appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>Where Holly and Mistletoe Are Typically Found
If you’re trying to find the difference between holly and mistletoe, look no further than where they grow. Holly typically grows on trees as dense bushes, while mistletoe is often found higher up, attached directly to tree branches.
Holly bushes have dark green, spiny leaves and bright red berries that birds love to eat. The berries may look tempting, but they can be poisonous to humans, so don’t eat them! Holly grows on its own roots in soil at the base of trees, unlike mistletoe which is parasitic.
Mistletoe, on the other hand, has soft, oval leaves and translucent white berries. It attaches itself to tree branches, absorbing water and nutrients from the tree. You’ll find mistletoe growing on deciduous trees like oak, maple and ash, especially in the upper branches.
Also Read > Difference Between Granuloma and Keloid
The next time you’re walking through the woods or your neighbourhood, look up and around. Do you see dense, spiny bushes growing around the base of trees, with red berries peeking through? Or do you spot green, leafy masses attached directly to treetops, with white berries? Whether it’s holly or mistletoe, they’re both festive symbols of winter and the season of giving.
The Cultural Significance and Practical Applications of Holly vs. Mistletoe
The cultural significance and uses of holly and mistletoe are quite different.
Holly is strongly associated with Christmas and winter festivities. Its bright red berries and spiny, evergreen leaves are used in wreaths, garlands, and other decorations to convey a feeling of warmth in the cold season. The Druids regarded holly as a sacred plant, believing it had magical powers that could ward off evil spirits during winter solstice celebrations.
In contrast, mistletoe has pagan origins and was used by the Druids in winter solstice rituals. They believed it promoted fertility, health and good luck. Today, mistletoe is commonly hung during Christmas time and used as an excuse for playful kissing under its leafy boughs.
While holly and mistletoe share a place in winter holiday traditions, they have very different practical uses: Hollywood is dense, hard and resistant to water, so it’s often used to make walking sticks, chess pieces, and tool handles. The leaves and berries can be used to make medicinal teas and tinctures.
Mistletoe, on the other hand, is a parasitic plant with white, sticky berries. The plant and berries are toxic to humans, so mistletoe is rarely used for any practical purpose. Some studies show mistletoe extracts may have anticancer effects, but more research is needed.
Whether for cultural traditions or practical uses, holly and mistletoe have enduring appeal. During the winter holidays, these festive plants conjure feelings of warmth, joy and goodwill.
Holly Vs Mistletoe

Holly
- Holly grows on trees, shrubs or as a standalone plant.
- Holly grows its own roots in the ground.
- Holly leaves are stiff, spiny and oval-shaped.
- Holly produces red berries. The holly berry is poisonous to humans if ingested.
- Holly flowers contain both male and female parts.
Mistletoe
- Mistletoe is parasitic, growing on tree branches.
- Mistletoe attaches itself to host trees, absorbing water and nutrients from the tree.
- Mistletoe leaves are smooth, oval and paired. Mistletoe leaves grow in pairs along the stem.
- Mistletoe berries are white or pink. The mistletoe berry is also toxic in large amounts.
- Mistletoe flowers are dioecious, meaning male and female flowers grow on separate plants.
In summary, while these two plants are frequently linked together during the holidays, holly and mistletoe actually have quite a few differences when you examine them closely. But no matter the differences, they both evoke the festive spirit of the season.
The post 5 Difference Between Holly and Mistletoe appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>The post 5 Difference Between AC and DC Current appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>One of the primary differences between alternating and direct current is that in alternating current, the polarity and magnitude of the current change at regular intervals, whereas in direct current, they remain constant. Some of these differences are discussed below.
What is Alternating Current
Alternating Current is what AC stands for. Alternating current, or AC, is a type of electric current whose strength changes all the time and whose direction changes from time to time. In practice, alternating current is generated by sources of alternating voltage, such as alternators and AC generators. The total quantity of time a waveform of alternating current takes to return to itself is known as the time period of the AC waveform.
Also Read > Difference Between Town and City
The frequency of an AC waveform is the rate at which the waveform repeats itself, or the number of cycles completed in one second. AC waveforms include sinusoidal AC, square wave, and triangular wave, among others. The AC is used extensively in our daily lives to power fans, bulbs, AC, laundry machines, etc.
What is Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is an electric current that only flows in one direction. It frequently consists of batteries, solar panels, and fuel cells and can power devices, recharge batteries, and start motors among other things.
DC has a voltage and current that stay the same over time. This means that the flow of electrons stays the same. This is different from alternating current (AC), which changes direction and has different levels of power and current. DC is often used in computer devices because it is simple and easy to work with. It’s easier to make and send because there’s no phase shift, and it’s also easy to change into other types of energy, like mechanical or heat energy.
AC Vs DC Current
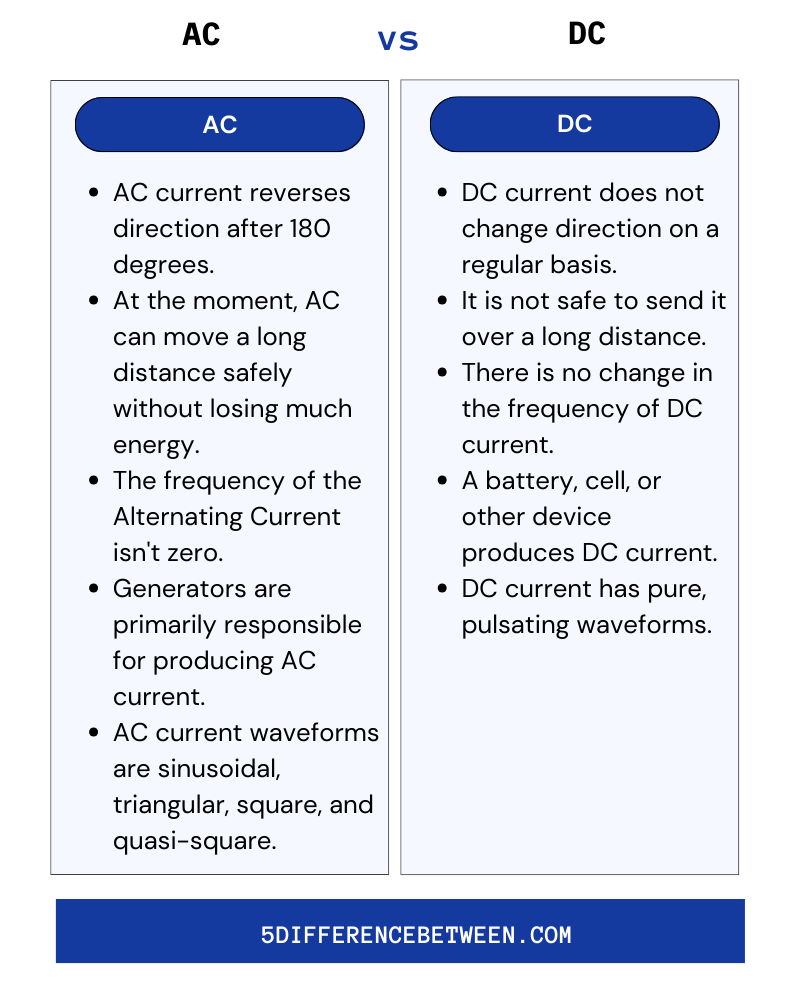
As stated above, there are many differences between alternating current and direct current. The precise details of AC and DC can be found in these differences. Both kinds of electric current are used for different things.
The post 5 Difference Between AC and DC Current appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>The post 5 Difference Between Percentage and Percentile appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>Defining Percentage and Percentile
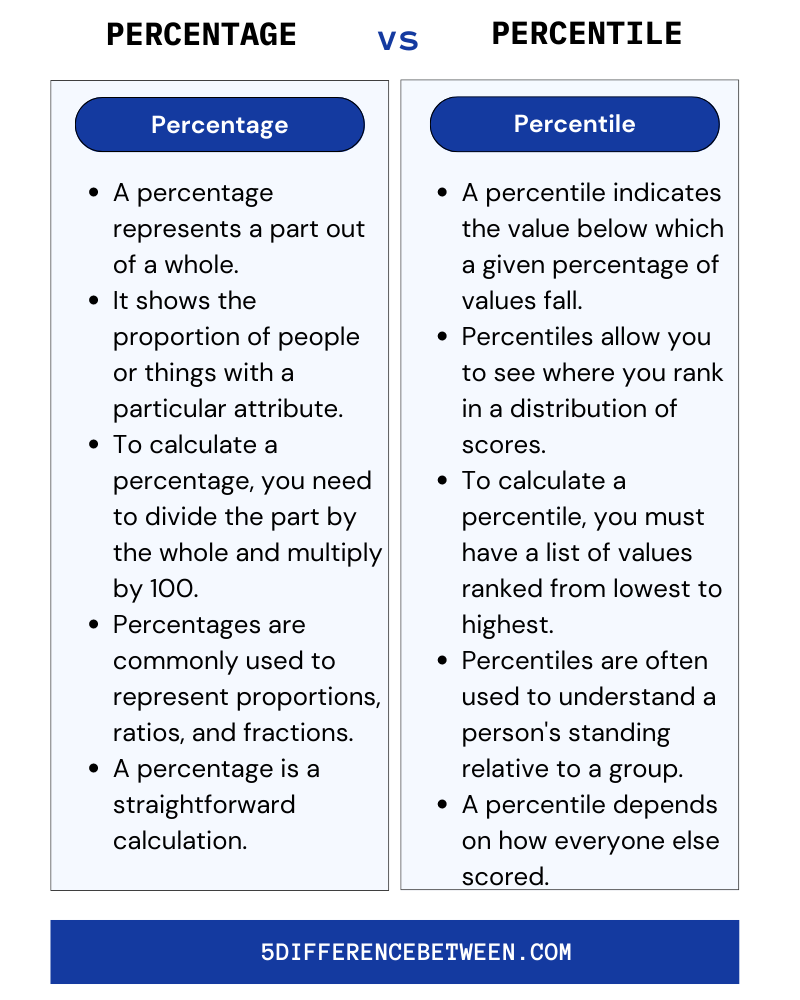
A percentage (%) represents a fraction of 100. For example, if 25 out of 100 students got an A on the test, that would be 25%. Percentages are used to indicate values relative to the whole.
A percentile basically indicates the percentage of scores that fall below a given score. For example, scoring in the 85th percentile means 85% of scores were lower than yours. Percentiles are used to show where a score falls in a distribution of scores.
Also Read > Difference Between Micro and Macro Economics
To calculate a percentage, you need to divide the part by the whole and multiply by 100. So if 30 students out of a class of 150 got an A, that’s 30/150 = 0.2 x 100 = 20%.
To determine a percentile, you need to know the distribution of all the scores. If a score is in the 80th percentile, then 80% of the scores are below that score. The scores are ranked from lowest to highest, and the percentile shows how a given score compares to all the others.
Percentages and percentiles are useful for comparing values and tracking progress. Just remember – a percentage represents a part out of a whole, while a percentile represents a value below which a certain percent of values fall.
Calculating Percentage vs Percentile
To understand the difference between percentage and percentile, let’s look at some examples.
A percentage (%) represents a fraction of 100. If you got 75% on a test, that means you earned 75 out of 100 points. Easy enough.
A percentile indicates the percentage of scores below a certain score. For example, scoring in the 80th percentile means you did better than 80% of other people who took the test. If 100 students took the exam and you’re in the 80th percentile, your score was higher than 80 of those students.
To calculate a percentile, you need to know the distribution of all the scores. The median score is right in the middle – half the scores are above and half below. Want to figure out what percentile a score of 85 is in? Count how many scores are 85 or below, divide that number by the total scores, and multiply by 100. If 40 out of 100 scores were 85 or less, 85 is in the 40th percentile (40/100 = 0.4 x 100 = 40th percentile).
Percentages and percentiles are related but different measurements. Both can be useful in understanding your performance and scores. Whether you’re focused on percentages, percentiles or both, keep working hard and improving!
Percentage Vs Percentile
A percentage and a percentile are two different measures, though they are often confused. Let’s look at the key difference between Percentage and Percentile:
While percentages and percentiles seem quite similar, it’s important to understand the distinction between these two useful measures. Knowing how they differ in calculation, definition, and use can help avoid confusion and allow you to apply them properly.
The post 5 Difference Between Percentage and Percentile appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>The post 5 Difference Between Accuracy and Precision appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>What is Accuracy
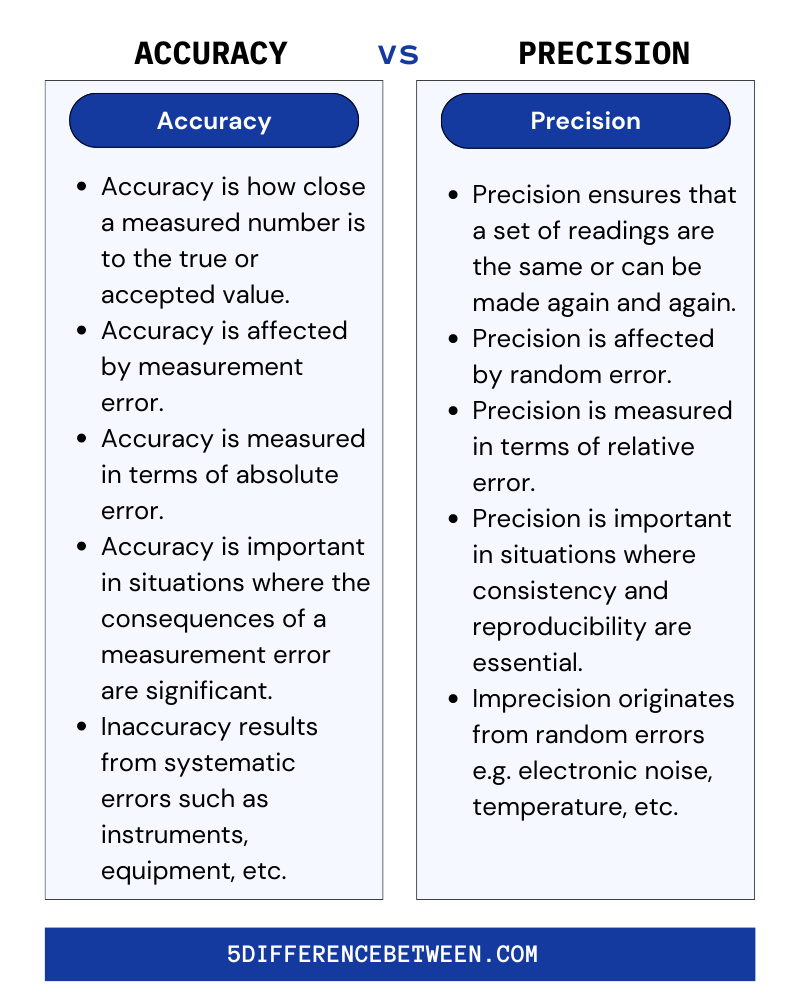
Accuracy is the degree to which a measured value or a set of observed values is close to something’s real value. So, the closer a measurement is to the real measurement of a thing, the more accurate it is. In the same way, accuracy is linked to how close something is to a specific point of reference or target.
Also Read > Difference Between Osmosis and Diffusion
How accurate something is depends on how well the measurement tools are set up. The less errors they have, and the more exact they are, the better they are calibrated.
What is Precision
In everyday life, the word “precision” is often used to mean “accurate.” But precision is how close the results of different measurements are to each other. Accuracy, on the other hand, is how close the value of a measurement is to the real value of what is being measured.
Repeatability is a very important part of being precise. That is, how often a set of measurements or actions are repeated, which means that the same thing is measured and done under the same conditions whenever the same tools are used.
Which is Important? Precision or Accuracy
When trying to hit a target, accuracy is more important. Either you hit the mark, or you don’t. It doesn’t help to be accurate if you never hit your target. Adding a correction factor to future measures can make them more accurate. If all your shots go to the left, try aiming to the right. You can make your measures more accurate in the future.
In math, accuracy is more important. When you use a measured value in a calculation, you can only be as exact as your least precise measurement. This is the main point of the topic of “significant numbers” in math. You can get more accurate by using a better measure tool or by getting better at using the one you have.
In science, good readings need to be both accurate and precise. In all your measures, try to make the best of both. But no matter how hard you try, measures will always be a little off from the correct amounts because of an error.
Accuracy VS Precision
In conclusion, accuracy and precision are two distinct concepts in measurement. Accuracy refers to how close a measured value is to the true value, while precision refers to the consistency or reproducibility of a set of measurements. Both are important in different contexts and can be affected by different factors. Understanding the differences between accuracy and precision is essential for making reliable and valid measurements.
The post 5 Difference Between Accuracy and Precision appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>The post 5 Difference Between Data and Information appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>What is data?
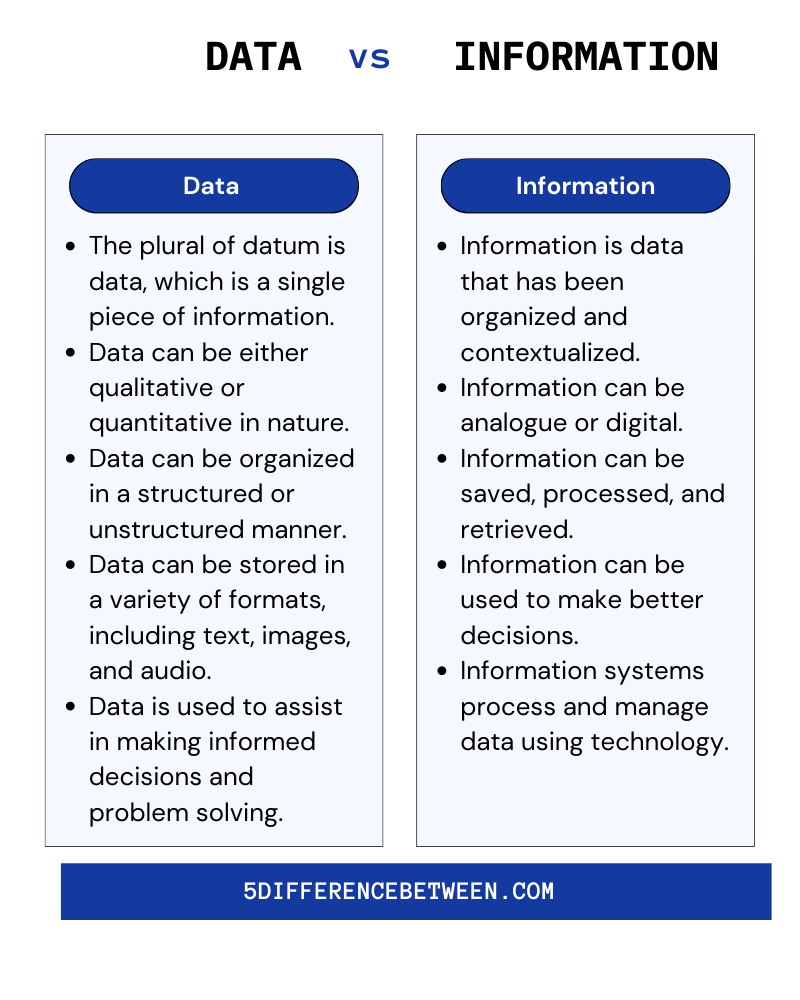
Data is information that has been gathered, organized, and analyzed for a particular purpose. Because it has not been processed or interpreted in any way, it is often referred to as raw or primary data. Data is used in a variety of fields, ranging from business and economics to science and engineering. Data is gathered from various sources, such as surveys, experiments, and observational studies. It can be numerical, textual, or visual, as well as structured or unstructured. Structured data is data that has been organized into a fixed field format, whereas unstructured data is data that has not been organized in any way. It’s also used to create new products and services, improve old ones, and conduct statistical analysis. The process of extracting meaning from data is known as data analysis. It entails using statistical techniques and algorithms to interpret data and identify patterns and trends. Data analysis can be used to develop models and simulations, as well as to interpret results and make decisions. They analyze data using a variety of tools and techniques such as machine learning, natural language processing, and deep learning.
Also Read > Difference Between Home and House
What is information?
Data that has been processed and organized in a meaningful way is referred to as information. It is the result of a system or process that adds value to data, allowing it to be used for decision making or other purposes. Text, images, audio, and video are all examples of information formats. It may also be quantitative or qualitative in nature. Information can be structured in various ways depending on its purpose, such as in a database, spreadsheet, or report. The key to knowledge is information. It can be used to gain a better understanding of systems and processes, assist in decision making, gain insight, and solve problems. It can also be used to forecast future trends, identify patterns and connections, and inform policy and strategy. Information is more accessible than ever before in the digital age, and it is increasingly being used to drive organizational innovation and improvement. As information becomes more interconnected, it can be shared and used in new ways.
Data Vs Information
Data and information are essential components of any organization or business. Although the terms are frequently used interchangeably, there are some significant differences between them.
Benefits of Data and Information
- The distinction between data and information can be subtle, but understanding it is critical. Data is an unprocessed collection of facts, figures, and statistics. It is also referred to as “bits and bytes,” and it serves as the foundation for all information. If you ask Recognizing and utilizing the difference allows organizations to gain insights into their operations and make better decisions. Understanding the distinction may aid organizations in better understanding and tracking their performance. Data analysis allows organizations to identify patterns, trends, and correlations. This can help them understand how their operations are performing and where they can improve.
- Data can also be used to improve report accuracy and timeliness. The ability to quickly gather, process, and analyze data can help organizations make more informed decisions. This allows organizations to save time and money by making more accurate predictions and decisions.
Finally, data is the starting point for the creation of information. Information is defined as processed data that is used to make decisions and solve problems. Information is structured and organized, whereas data is disorganized and unstructured.
The post 5 Difference Between Data and Information appeared first on 5 Difference Between.
]]>