Family medicine and internal medicine are two medical specialties that frequently overlap but differ significantly. Looking for what is the difference between family medicine and internal medicine? Internal medicine focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of more serious or complex medical conditions, whereas family medicine focuses on overall health maintenance and disease prevention. Both are required for medical practice and contribute to patients’ overall health. We will now understand the difference between family medicine and internal medicine.
What is Family Medicine?
To understand the Internal Medicine Versus Family Medicine differences it is essential to know them well. Family medicine is a medical specialty that focuses on the comprehensive health care of individuals and families across all ages, genders, organs, and body systems. It is the medical specialty devoted to the comprehensive care of the individual and the family in health and in illness. Family medicine combines scientific knowledge and clinical expertise to provide continuing and comprehensive health care to each member of the family.
Also Read > Difference Between Vegan and Vegetarian
The physicians are trained to diagnose, treat, and manage a broad range of conditions affecting people of all ages. They are trained to provide preventive health care, diagnose and treat acute and chronic illnesses, provide medical care for the entire family, and refer patients to specialists when necessary. They also provide management of chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity.
Also the physicians are trained to provide preventive care such as routine check-ups, health screenings, immunizations, and patient education. They are also trained to recognize the importance of lifestyle choices and preventive care in maintaining health and preventing disease. They provide counseling and support to help patients make positive lifestyle changes.
How Does It Benefit People?
Family medicine is a medical specialty that focuses on providing comprehensive healthcare for the entire family. It is a comprehensive approach to health care, which means that it covers a wide range of medical issues. This includes diagnosis and treatment of acute illnesses, preventive care, and management of chronic health problems. The goal of family medicine is to provide comprehensive and coordinated care that meets the needs of the entire family.
Family medicine provides patients with an interdisciplinary approach to healthcare. This means that the physician is responsible for coordinating care among specialists in different fields, such as cardiologists, endocrinologists, neurologists, and psychologists. This allows the patient to receive the most comprehensive care possible.
Family medicine also helps patients stay healthy. Through preventive care, patients can be monitored for any signs of health problems before they become serious. This includes regular physical exams and screenings to detect any possible signs of illness or disease. In addition, family medicine providers can help patients develop healthy lifestyle habits, such as exercising, eating healthy, and avoiding smoking and drinking.
What is Internal Medicine?
Internal Medicine is a branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases in adults. It involves the diagnosis, management, and prevention of diseases affecting the internal organs, such as the heart, lungs, brain, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract. It is a specialty that provides comprehensive medical care to adults, including diagnosis and management of complex medical issues and prevention of acute and chronic diseases.
The physicians are trained to diagnose, manage, and treat a wide range of medical issues. They are trained in both the medical and surgical aspects of internal medicine. This includes diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases of the internal organs, such as the heart, lungs, brain, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract. Additionally, they are trained in preventive medicine and in the management of chronic conditions.
The practice of internal medicine includes diagnosing, managing, and preventing diseases, as well as providing patient education, physical examinations, and health screenings. Internal medicine physicians may also prescribe medications, perform minor surgeries, and refer patients to other specialists. They typically coordinate care with other medical professionals and may provide primary care services such as check-ups and routine health screenings.
Benefits of Internal Medicine
Internal medicine is a field of medicine that focuses on the prevention and treatment of adult diseases. It is a specialty that focuses on the diagnosis and nonsurgical treatment of diseases that affect adults. It is also known as general medicine, as it covers a wide range of conditions, including common and rare illnesses. Internal medicine physicians have a unique set of skills that can benefit both their patients and their practice. They are trained to diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions and diseases, from simple to complex. They are often the first point of contact for patients, making them a valuable asset in any medical practice.
Internal medicine physicians are also well-versed in preventive care and can provide comprehensive care to their patients. They focus on prevention and early detection of diseases, helping to reduce the risk of illnesses and complications. Furthermore, they are adept at coordinating care between multiple medical specialists, providing patients with a more comprehensive and holistic approach to their healthcare.
Family Vs Internal Medicine
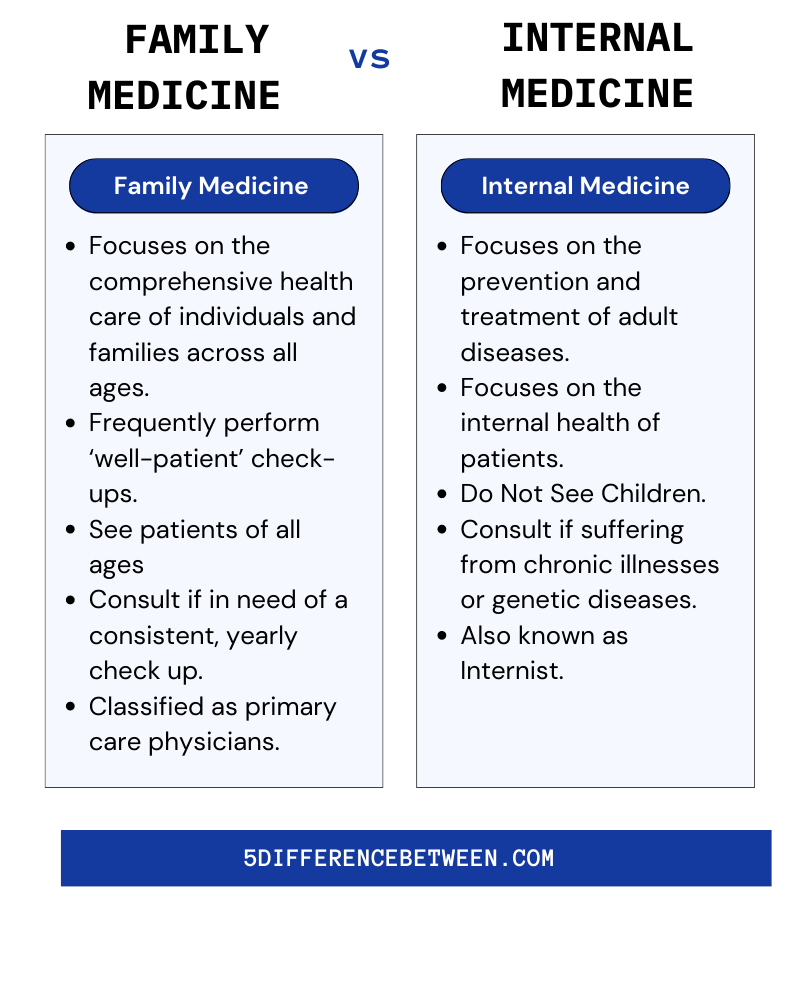
Difference between family medicine and internal medicine can be defined as that doctors of family medicine are primary care physicians who can diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions. Internal medicine physicians, on the other hand, specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases and conditions that affect the body’s internal organs and systems. Both specialties are important and provide critical care to patients. Finally, the physician’s personal preferences and skills influence his or her specialty choice.