The two types of cells found in the living world are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are the most fundamental type of cell, found in both unicellular and multicellular organisms. They are typically smaller than eukaryotic cells and have simpler structures. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, are more complex and found in more complex organisms such as plants and animals. This article will go over the major differences between the cells.
What are Prokaryotic Cells ?
Prokaryotic cells are the most fundamental and widespread type of living cell. They are single-celled organisms found in nearly every environment on Earth, from the highest mountain peak to the ocean floor. They can exist as single organisms or in colonies, and their sizes range from 0.2 to 10 micrometers. Prokaryotes are typically unicellular, consisting of only one cell. Because their DNA is not bound by a nuclear membrane, it is not separated from the rest of the cell. A nucleoid region, on the other hand, holds the DNA together. Prokaryotes can reproduce quickly, and many species can adapt to different environments. They play an important role in the ecosystem because they control decomposition and nutrient cycling.
Also Read > Difference Between Mitosis and Meiosis
What are Eukaryotic Cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that is surrounded by a membrane and contains genetic material. These cells, which can be found in organisms such as plants and animals, are far more complex than prokaryotic cells. They also have additional organelles, allowing for greater complexity and specialization. Organisms include mitochondria, chloroplasts, the Golgi apparatus, and the endoplasmic reticulum. Because they contain more genetic material and organelles, eukaryotic cells are significantly larger than prokaryotic cells. They also have a cytoskeleton for movement and a cell wall for protection. Eukaryotic cells are the most complicated and important type of cell.
Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller than eukaryotic cells.
- Prokaryotic cells reproduce primarily through binary fission whereas eukaryotic cells reproduce through the process of mitosis.
- Prokaryotic cells are simpler than eukaryotic cells because they lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
- In Prokaryotic cells mitochondria is absent whereas in eukaryotic cells mitochondria is present.
- Circular DNA is found in prokaryotic cells, whereas linear DNA is found in eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells
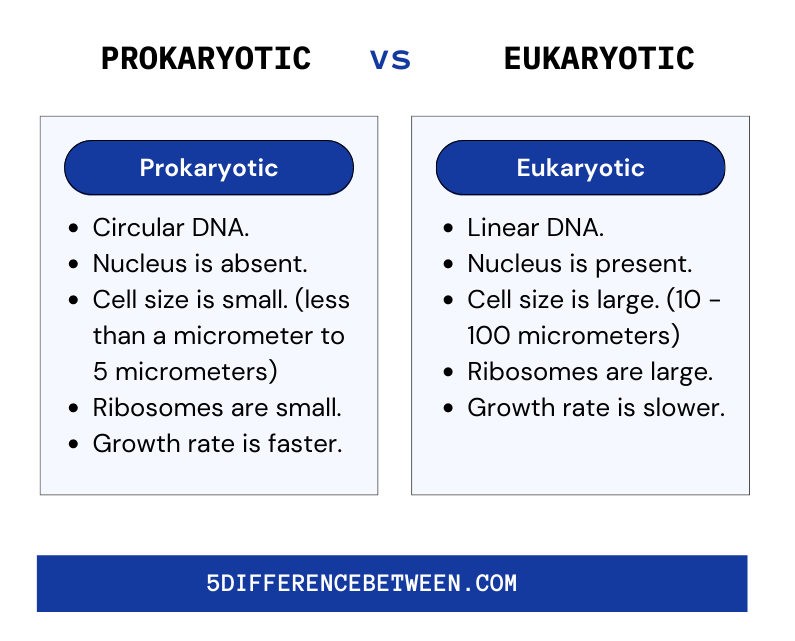
The major difference between the cells is that Eukaryotic cells are more complex and larger than prokaryotic cells. They have a single circular chromosome, no nucleus, and no other organelles. Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex because they have a nucleus and other organelles, as well as linear chromosomes. Cell membranes, ribosomes, and DNA are present in both types of cells, but their structures and functions differ. Finally, nuclei and organelles are the most noticeable differences between these cells in size, complexity, and structure.