You awaken with odd, itchy bites throughout your body. Ugh, what’s going on? Could it be those dirty bed bugs you’ve heard so much about? Or perhaps you’re managing dust mites, and microscopic critters that live on your bedding. Even as each can cause skin infection, bed bugs and dust mites have key differences. Read on to learn how to tell these nighttime nuisances apart. Attending to the bottom of your biting mystery will help you discover the proper solution and get a terrific night time’s sleep again.
What Are Bed Bugs
Bed bugs are little, oval, caramel parasitic bugs that feed on human blood. About the size of an apple seed, bed bugs are striking drifters and could without inconvenience pass gradually into your stuff, clothing, bedding, and decorations.
Adult bed bugs have flat bodies, and six legs, and are visible to the bare eye. After feeding, their bodies swell and grow to be shiny red. Bed bugs undergo multiple nymphal stages before turning into adults. Female mattress bugs can lay 200 to 500 tiny white eggs, which hatch in about a week. Bed bugs are maximum energetic at night after they emerge from hiding spots to feed.
Also Read > Difference Between Terminal Voltage and EMF
The most obvious sign of bed bugs is bites of your pores and skin. Their bites often seem like small, red, itchy welts, commonly on exposed skin just like the face, neck, and palms. But some humans do not react to the bites in any respect. While bed bugs are a nuisance, they are no longer acknowledged to spread disease. However, their bites can result in secondary infections if scratched excessively. A few humans also experience anxiety, strain, and insomnia from residing with a bed bug infestation.
Bed bugs no longer fly or soar. They move slowly at a pretty accurate clip over floors, walls, and ceilings. Bed bugs generally inhabit bedrooms and living rooms, hiding for the duration of the day in dark, undisturbed places close to where humans sleep.
The key to controlling bed bugs is early detection and a comprehensive pest control approach. Analyzing for signs and symptoms of an infestation and decreasing clutter where mattress insects can cover are important first steps to getting rid of these parasitic pests.
What Are Dust Mites
Dust mites are tiny bugs that feed on dead skin cells and different organic memories. They’re located in household dust and like warm, humid environments. Unlike bed bugs, dust mites don’t chunk human beings. Yet, their droppings and shed skin can cause sensitivities, asthma signs and side effects in loads of individuals.
Dust mites flourish in locales of your confidential home which are inadequately ventilated and sticky, along with bedrooms, rugs, bedding, upholstered furniture, and jumbled garage regions. They want humidity ranges of at least 50-60% to continue to exist and reproduce. Excessive warmness and occasional humidity conditions are not suitable for dust mites. If humidity is controlled, their numbers can be minimized.
Dust mites acquire moisture and vitamins from ingesting dead skin cells, puppy dander, fungi, pollen, and bacteria. A single dust mite can produce up to 20 droppings in keeping with the day, and each carries proteins that cause allergic reactions and asthma symptoms in sensitive individuals. Their droppings and shed skins are acquired in dirt and are a main contributor to allergens in the domestic.
Some steps you can take to reduce dust mites in your property consist of:
- Encase mattresses, pillows and comforters in protecting covers which might be mainly designed to block dust mites.
- Wash all bedding weekly in warm water (at a minimum of 130 F) to kill dust mites and remove allergens.
- Reduce indoor humidity to below 50% using an air conditioner or dehumidifier.
- Vacuum carpets, rugs, naked flooring and upholstered furniture regularly use a vacuum with a HEPA clear out to capture small debris.
- Remove clutter where dust collects.
- Bathe pets weekly to minimize dander.
- Consider proficient steam cleaning floor coverings and upholstery.
By controlling mugginess, lessening food sources, and rehearsing great housekeeping, you can restrict dust mite populaces and limit sensitivity and asthma side effects in your home.
Bed Bugs Vs Dust Mites
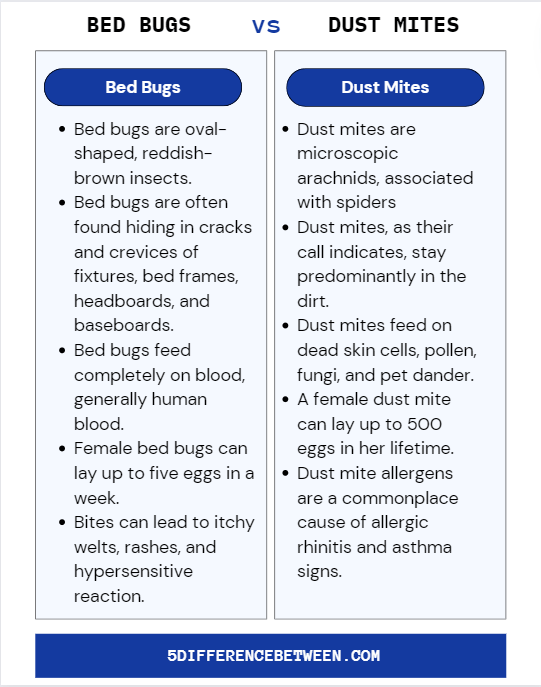
Bed Bugs
- Bed bugs are oval-shaped, reddish-brown insects which can be visible to the naked eye, approximately the size of an apple seed.
- Bed bugs are often found hiding in cracks and crevices of fixtures, bed frames, headboards, and baseboards.
- Bed bugs feed completely on blood, generally human blood.
- Female bed bugs can lay up to five eggs in a week and more than five hundred eggs in their lifetime.
- Bed bug bites can lead to itchy welts, rashes, and hypersensitive reactions in some people.
Dust Mites
- Dust mites are microscopic arachnids, associated with spiders. You may need a magnifying glass to see them.
- Dust mites, as their call indicates, stay predominantly in the dirt.
- Dust mites feed on dead skin cells, pollen, fungi, and pet dander.
- A woman dust mite can lay up to 500 eggs in her lifetime.
- Dust mite allergens, determined by their feces and body parts, are a commonplace cause of allergic rhinitis and asthma signs.






