Have you ever had a bump under your pores and skin that simply did not seem to move away? You possibly assumed it was just an innocent fatty tumor known as a lipoma. However, how are you going to tell if it is sincerely some element extra serious – like a liposarcoma? Do not freak out just yet. Even as both lumps are made from fat cells, there are a few key versions between these growths. Studying this will help you understand what’s lurking under your skin and when it’s time to get checked out.
What is a Lipoma?
A lipoma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor made up of fat cells. Lipomas are typically soft, movable lumps located just under the skin. They are the most common tender tissue tumor. Lipomas normally grow very slowly and seldom cause pain or discomfort.
Lipomas can increase anywhere on the body but are usually found on the neck, top torso, upper arms, and thighs. They are generally spherical or oval in shape and sense doughy or spongy. Lipomas are normally small, measuring much less than two inches in diameter, but in a few cases can come to be pretty massive.
Also Read > Difference Between Bed Bugs and Dust Mites
The purpose of lipomas isn’t always absolutely understood but is thought to involve an aggregate of genetic elements and harm or injury to fat cells. Lipomas tend to run in families and frequently appear throughout mid-maturity, between 40 to 60 years of age. But, they can develop at any age.
Diagnosis & Treatment
Lipomas are commonly identified based totally on a physical examination and scientific history. The health examiner will observe the lump for traits ordinary of a lipoma, which include its soft, doughy feel; capability to move effortlessly; increased pattern; and location. Imaging checks like an ultrasound, CT or MRI scan may additionally from time to time be used to verify the prognosis or decide the quantity of a huge lipoma. A biopsy is generally not needed unless the lump has uncommon features or is no longer cut back with steroid injections.
Lipomas themselves are normally harmless and do not require remedy. However, removal can be endorsed if the lipoma is massive, reasons soreness or affects movement. Surgical excision, liposuction, and steroid injections are alternatives for getting rid of or reducing lipomas. Recurrence after removal is uncommon but possible. Standard self-tests and specialist visits can assist with identifying any new or concerning lumps so you get proper consideration.
What Is Liposarcoma?
Liposarcoma is an uncommon sort of cancer growth that is created in fat cells. Not at all like harmless lipomas, liposarcomas are threatening growths, meaning they can spread to different parts of the body. Liposarcomas normally foster in the fat tissues of the appendages, stomach cavity, or behind the peritoneum (the lining of the abdomen).
There are a few subtypes of liposarcomas, including very much separated, myxoid, pleomorphic, and dedifferentiated. Well-separated liposarcomas will grow more often than not develop gradually and can repeat over and over. Myxoid liposarcomas are more normal in more youthful grown-ups and frequently fostered in the thighs. Pleomorphic liposarcomas are the most forceful sort and ordinarily emerge in the limits. Dedifferentiated liposarcomas emerge from all-around separated growths and become high-grade, quickly developing cancers.
Liposarcomas frequently don’t cause side effects in the beginning phases. As the tumor develops, it might cause a noticeable expansion or bump. Pain, particularly assuming the mass is enormous or proceeds encompassing tissues, can likewise happen. To confirm the finding, your doctor will play out a biopsy to look at the growth cells. Imaging tests like CT or X-ray scans may likewise be utilized to decide the cancer size and assume it has spread.
Diagnosis & Treatment
The principal medicines for liposarcoma include:
Medical procedure to eliminate the tumor: This might include appendage saving a medical procedure or removal depending upon the cancer size and area. Radiation treatment is much of the time given previously or after a medical procedure.
Radiation treatment: High-energy radiates are utilized to kill cancer growth cells. It could be utilized alone or with a medical procedure.
Chemotherapy: Anti-cancer disease drugs are utilized to obliterate tumor cells. Chemotherapy is in many cases used to treat metastatic or repeating liposarcomas.
Targeted drug treatment: More up-to-date tranquilizers that target explicit atoms inside cancer cells might be possibilities for certain patients.
Lipomas Vs Liposarcomas
Lipomas and liposarcomas can appear to be comparable from the start, yet there are a few vital contrasts to know about.
Lipomas
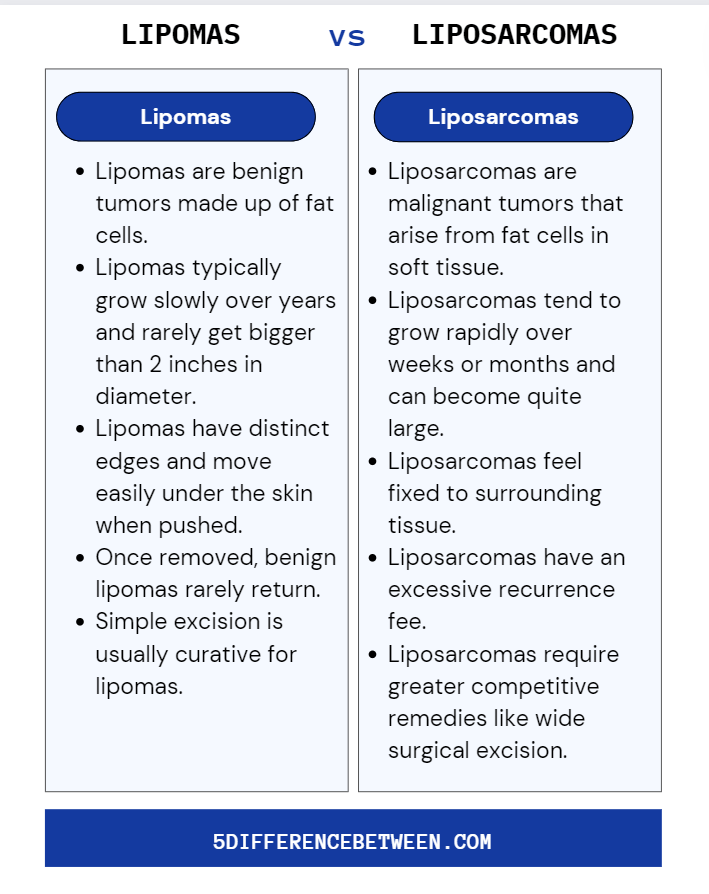
- Lipomas are benign tumors made up of fat cells.
- Lipomas typically grow slowly over years and rarely get bigger than 2 inches in diameter.
- Lipomas have distinct edges and move easily under the skin when pushed.
- Once removed, benign lipomas rarely return.
- Simple excision is usually curative for lipomas.
Liposarcomas
- Liposarcomas are malignant tumors that arise from fat cells in soft tissue.
- Liposarcomas tend to grow rapidly over weeks or months and can become quite large.
- Liposarcomas feel fixed to surrounding tissue.
- Liposarcomas have an excessive recurrence fee, even with remedies like surgical operation, radiation or chemotherapy.
- Liposarcomas require greater competitive remedies like wide surgical excision.
In summary, the differences in composition, increase, mobility, recurrence risk, and required remedy set lipomas and liposarcomas aside. While lipomas are usually innocent and easy to eliminate, liposarcomas must be taken very seriously because of their malignant nature. Consulting with a doctor is imperative to decide the appropriate next steps.