With an understanding of how primary and secondary memory interact, you’ll be better equipped to keep your computer’s memory in balance and running smoothly. And when it comes to your computer’s performance, every little bit of knowledge helps!
Primary Memory: RAM and ROM
Your computer has two types of memory: primary and secondary. Primary memory, also known as main memory, refers to RAM and ROM.
RAM, or random access memory, is your computer’s short-term memory. It temporarily stores information your computer needs right now to run programs and applications. RAM is fast but volatile, meaning it loses data when the computer is turned off.
Also Read > Difference Between Cotton and Nylon
ROM, or read-only memory, contains important instructions to operate your computer. ROM is non-volatile, so it retains data even without power. ROM includes your computer’s BIOS, which helps boot up your machine.
Primary memory is faster than secondary memory (like your hard drive) but more expensive, so computers usually have less primary memory. If your computer runs out of primary memory, it has to swap data between the primary and secondary storage, which really slows things down.
Secondary Memory: Hard Drives and Flash Drives
Secondary memory is storage that persists even when your device is powered off. The two most common types are hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid state drives (SSDs), like flash drives and SD cards.
HDDs have spinning magnetic disks that store your data. They’re cheap but slower and more fragile. SSDs actually use flash memory chips with no moving parts. They’re faster, lighter, and more durable but typically cost more.
For most people, an SSD is the way to go these days for your main storage. Prices have dropped a ton, and the speed and reliability benefits are huge. If you need a lot of storage for things like photos, videos, or music, an HDD is still a good, affordable option. You can also use a smaller SSD for your operating system and main programs, then have an HDD for your personal files.
Primary Memory Vs Secondary Memory
The primary and secondary memory work together, but have some key difference between primary and secondary memory.
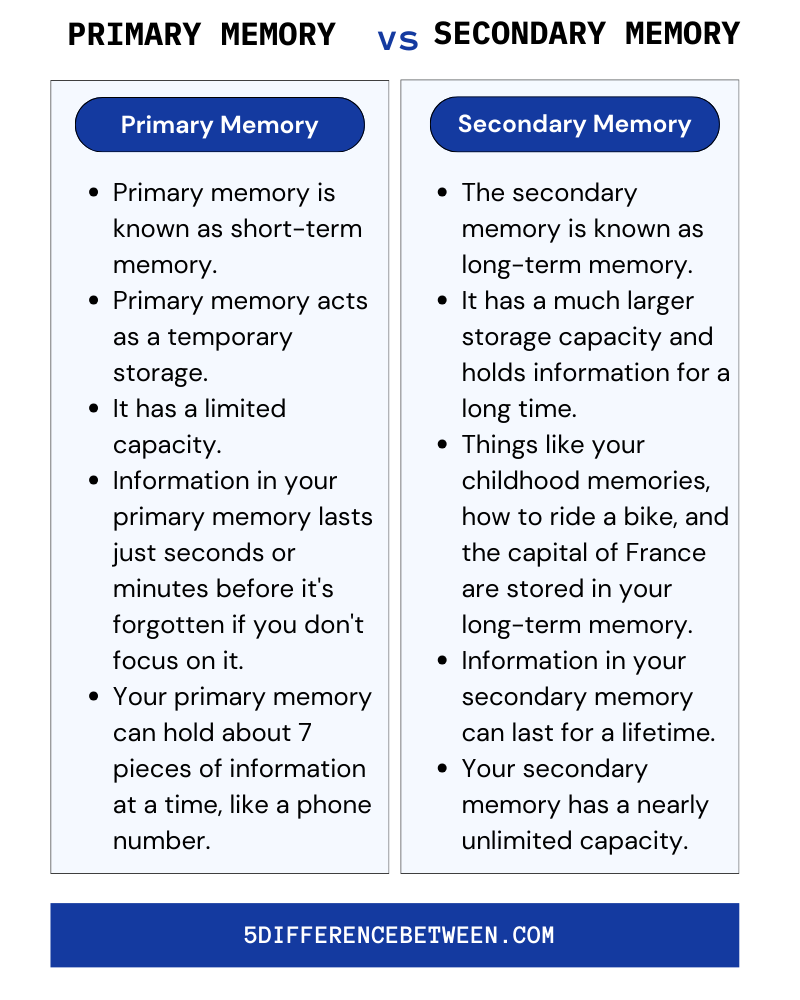
Primary Memory
- Primary memory is known as short-term memory.
- Primary memory acts as a temporary storage for information you’re actively using like a phone number you’re about to dial or directions you’re following.
- It has a limited capacity and things are quickly forgotten if not rehearsed or transferred to your secondary memory.
- Information in your primary memory lasts just seconds or minutes before it’s forgotten if you don’t focus on it.
- Your primary memory can hold about 7 pieces of information at a time, like a phone number.
Secondary Memory
- The secondary memory is known as long-term memory.
- It has a much larger storage capacity and holds information for a long time.
- Things like your childhood memories, how to ride a bike, and the capital of France are stored in your long-term memory.
- Information in your secondary memory can last for a lifetime.
- Your secondary memory has a nearly unlimited capacity and contains a lifetime of memories and knowledge.
While there is some clear difference between primary and secondary memory, they work closely together. Your primary memory takes in information from your senses and either discard it quickly or passes it along to your secondary memory for long-term storage through rehearsal and consolidation. Together, they make up your ability to remember, learn, and thrive.






