You’ve presumably heard the Torah alluded to as the law of Moses or the Five Books of Moses, yet there’s something else to comprehend. The Torah is the fundamental text of Judaism, recording God’s disclosure to Moses at Mount Sinai and the early history of the Jewish public. The Talmud, then again, is an assortment of rabbinic lessons and understandings of the Torah that fills in as the reason for Jewish regulation and custom. While the Torah is composed of regulation, the Talmud grows and clarifies that regulation to direct Jewish practice. Read on to explore the Torah vs Talmud and deepen your understanding of Judaism’s most sacred texts.
The Torah: The Foundation of Judaism
The Torah, Judaism’s most sacred text, contains the first five books of the Hebrew Bible. These books establish the laws and beliefs of Judaism.
The Torah presents primary stories, similar to God making the world in six days, Noah and the extraordinary flood, and the departure of the Israelites from Egypt. The Torah lays out Jewish occasions like Passover, Shavuot, and Sukkot.
Also Read > Difference Between Satin Nickel and Brushed Nickel
For Jews, the Torah is the heavenly expression of God. It’s studied, chanted, and revered. Duplicates of the Torah scroll are kept in the ark of each and every place of worship.
The Torah gives the premise to all Jewish convictions and practices. It has endured for millennia and remains sacred and relevant to Jews today when it was given to Moses at Mount Sinai. Studying the Torah is a lifelong pursuit for religious Jews seeking to understand God’s teachings fully.
So in summary, the Torah contains the foundational teachings of Judaism. It introduces core beliefs, establishes laws and mitzvot, and provides a glimpse into the earliest Jewish stories. For strict Jews, the Torah is the exacting expression of God and a wellspring of nonstop review and motivation.
The Talmud: An Analysis and Interpretation of the Torah
The Talmud is quite possibly one of the main strict texts in Judaism. It’s an assortment of discourses and conversations on the Torah by old Jewish researchers. The Talmud examines, deciphers, and applies the laws of the Torah to life’s regular circumstances.
Unlike the Torah, which contains the written law of God, the Talmud expands on these laws through debates and stories. It covers everything from civil and ceremonial law to ethical and moral teachings. For religious Jews, the Talmud is a practical guide for living according to God’s will.
The Talmud is massive, spanning over 6,000 pages in printed form. It covers 39 broad subject areas, ranging from agriculture and prayers to women’s rights and criminal law. For each area, the Talmud presents various opinions from respected rabbis. It’s meant to be studied and debated, not just read.
For religious Jews, studying the Talmud is a lifetime endeavour. It’s a method for acquiring further knowledge of Jewish regulations and morals. The Talmud has likewise affected Jewish culture, values, and personality. However perplexing, it gives direction on the best way to carry on with a significant and equitable life as indicated by Jewish practice.
Torah Vs Talmud
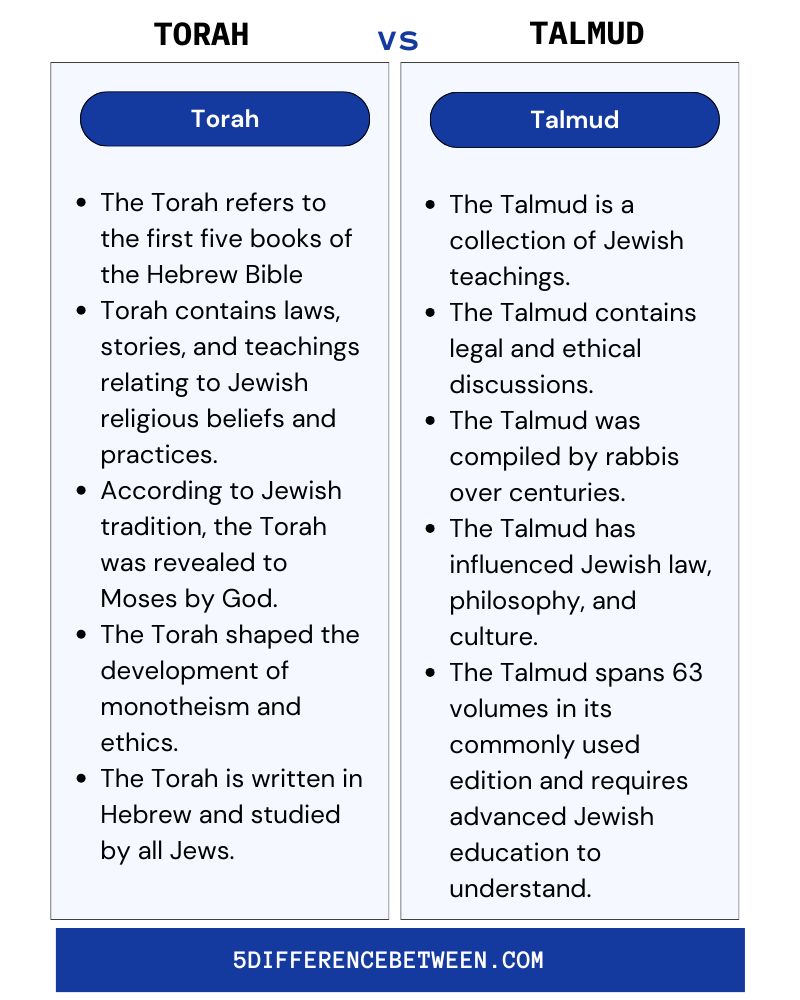
Torah
- The Torah refers to the first five books of the Hebrew Bible
- Torah contains laws, stories, and teachings relating to Jewish religious beliefs and practices.
- According to Jewish tradition, the Torah was revealed to Moses by God.
- The Torah shaped the development of monotheism and ethics.
- The Torah is written in Hebrew and studied by all Jews.
Talmud
- The Talmud is a collection of Jewish teachings that expand on and interpret the Torah.
- The Talmud contains legal and ethical discussions, folklore, and stories that apply Torah laws to everyday life.
- The Talmud was compiled by rabbis over centuries, with the final version published around 500 CE.
- The Talmud has influenced Jewish law, philosophy, and culture.
- The Talmud spans 63 volumes in its commonly used edition and requires advanced Jewish education to understand.
The Torah and the Talmud are the most important religious texts in Judaism, but they differ in significant ways.




