Endothermic and exothermic reactions are chemical reactions that differ in terms of heat absorption and release. Exothermic reactions emit heat energy into their surroundings, whereas endothermic reactions absorb heat energy from them. This article will go over the distinctions between endothermic and exothermic reactions.
To know more about the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions it is better to know what they are individually.
What is Endothermic Reaction?
Endothermic reactions are chemical reactions that absorb energy in the form of heat from their surroundings. These reactions typically involve the breaking of chemical bonds, which necessitates the use of energy. The overall reaction is exothermic, which means it produces heat, but it produces less heat than it absorbs from the environment. These reactions are important in many areas of chemistry, including fertilizer production and fuel production. They are also important in biology because many chemical processes that occur in living organisms are endothermic.
Also Read > Difference Between Compound and Mixture
They occur when two molecules react and form a new bond. Energy is absorbed from the environment during this process, causing the reactants to combine to form a new product. This energy can manifest as heat, light, or both. Because of the absorbed energy, the reactants break and form new bonds, yielding the desired product. The amount of energy absorbed by an endothermic reaction is typically greater than the amount of energy released. This is why endothermic reactions are frequently used to reduce a system’s temperature. When the reaction occurs, the heat absorbed exceeds the heat released, causing the temperature of the system to drop.
What is Exothermic Reaction?
An Exothermic reaction is a type of chemical reaction that produces heat as a byproduct. This heat energy is released into the environment as light, sound, or heat. These reactions are diametrically opposed to endothermic reactions, which absorb energy from their surroundings. These reactions are extremely common in everyday life and can be observed in a wide range of situations.
The energy released in exothermic reactions is greater than the energy absorbed. This energy is released as heat, allowing the reaction to self-sustain. As a result, the reaction will proceed until all of the reactants have been consumed. They are classified into two types: exergonic and endergonic. Exergonic reactions are those that produce more energy than they consume. These reactions are usually spontaneous, and they will continue until all of the reactants have been consumed. In contrast, endergonic reactions absorb more energy than they release. These reactions are usually not spontaneous and require an energy input to begin.
Further they have a wide range of applications. They are used in power plants to generate electricity as well as to produce fuels such as gasoline. They are also used in a variety of everyday activities such as cooking and heating. Exothermic reactions are used in the medical field to sterilize medical equipment as well as to create drugs and vaccines. Exothermic reactions are a type of chemical reaction that can produce energy or other useful materials. They are a common part of daily life and can be used for a variety of purposes. Understanding how these reactions work can help us use them more effectively in our daily lives.
Endothermic Vs Exothermic Reaction
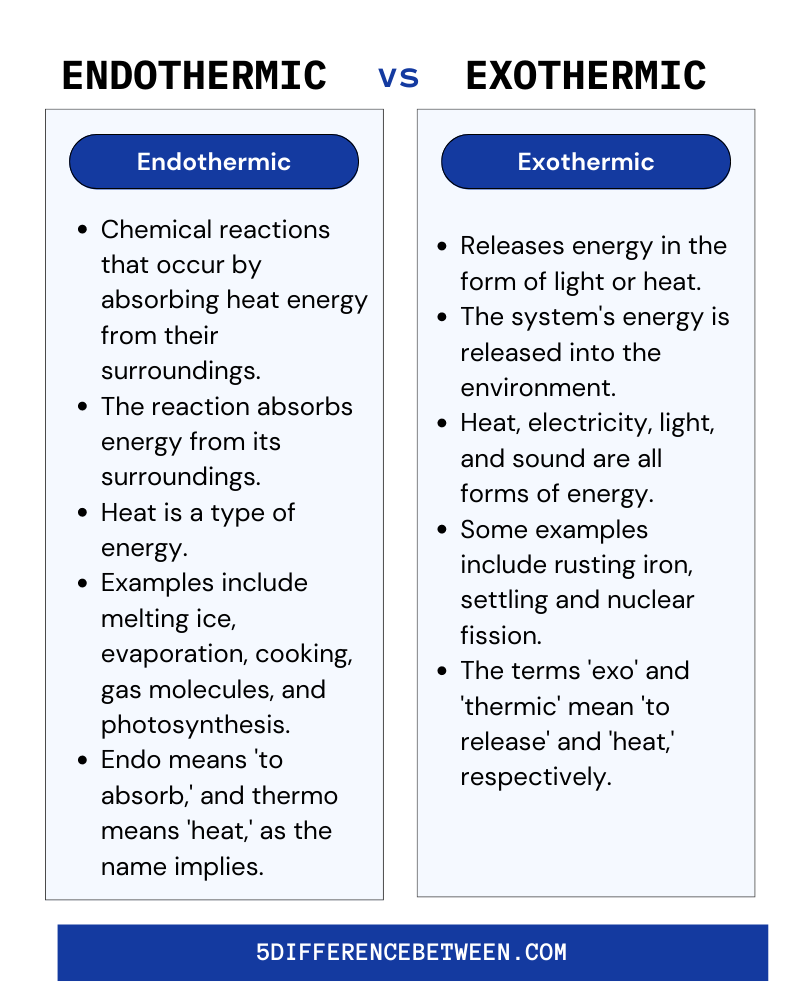
Exothermic and endothermic reactions are chemical reactions that either release or absorb energy. Exothermic reactions produce heat, light, or sound, whereas endothermic reactions absorb energy. Understanding which reactions are exothermic and which are endothermic is critical for predicting reaction outcomes and controlling the amount of energy released or absorbed.