You’ve possibly heard of ablation and coagulation if you or a person you already know has had heart surgical treatment. However, do you surely understand the difference between those two approaches? At the same time as they both deal with doing away with defective electrical pathways for your heart, the techniques and effects may be pretty exclusive. Understanding how they work could literally save your life one day if your doctor recommends one over the other. Arm yourself with knowledge so you can make the best decision about any future cardiac procedures your physician advises.
What Is Ablation?
Ablation is a minimally invasive surgical operation used to break tissue in a controlled process. The term comes from the Latin phrase ‘ablatio’ meaning ‘removal’. All through ablation, a tool like a laser, radiofrequency electrode or cryoprobe is used to precisely target and spoil diseased tissue without negatively surrounding healthy tissue.
Also Read > Difference Between Open and Closed Mitosis
Types of Ablation Procedures:
Radiofrequency Ablation: Uses high-recurrence electrical flows to produce intensity and crush abnormal tissue like cancers or heart arrhythmias. Consistently used to treat liver or kidney diseases.
Laser Ablation: Focusses excessive light power to vaporize tissue. Used for processes like disposing of varicose veins or precancerous skin lesions.
Microwave Ablation: Uses microwave energy to generate heat and damage tissue. Can be used to deal with small tumors in organs like the liver, lung or bone.
Cryoablation: Uses extremely bloodless temperatures to freeze and destroy atypical tissue. Often used to deal with certain varieties of cancerous or precancerous tumors.
The primary advantages of ablation are that it avoids the want for open surgical operation, causes minimal damage to healthy tissue, reduces aches and scarring, and allows for quicker restoration. However, ablation may not eliminate the targeted tissue as thoroughly as surgical removal. It additionally includes dangers like infection, blood clots and damage to nearby organs or blood vessels.
While finding out between ablation and extra-invasive surgeries, you and your physician need to reflect on consideration factors like the location, size and form of tissue being treated, your ordinary fitness, and the dangers and benefits of each choice. Ablation can be a very good choice for some conditions, however, surgical procedures can also nevertheless be needed in positive situations. Close monitoring is required after any procedure to ensure maximum effectiveness.
What Is Coagulation
Coagulation includes using warmness or electrosurgical devices to stop bleeding through surgical treatment or other medical tactics. Coagulation works by using adverse blood vessels and tissue to seal them off, which enables the manipulation of blood loss. The most usual kinds of coagulation used are electrocautery and radiofrequency ablation.
Electrocautery makes use of electric-powered modern hands through a small probe to generate warmness and seal tissue. It’s commonly used all through surgical operations to control bleeding from small blood vessels. The electric current causes the blood proteins to fuse together, blocking the blood vessels. This helps reduce blood loss during procedures. Electrocautery can also be used to seal lymph vessels and nerves.
Coagulation techniques are very effective at controlling bleeding and sealing tissue during medical procedures. They minimize blood loss and the need for blood transfusions. While coagulation does destroy some healthy tissue, it only affects a small area. The damage is also minimal compared to open surgery. Recovery times tend to be faster with less pain, scarring, and risks of complications.
Coagulation is a flexible device used in many areas of medicine. Understanding the difference between the options permits you to pick out the most effective and minimally invasive treatment for your condition. Discussing the pros and cons of each approach together with your health practitioner will make certain you get the first-rate consequences feasible.
Ablation Vs Coagulation
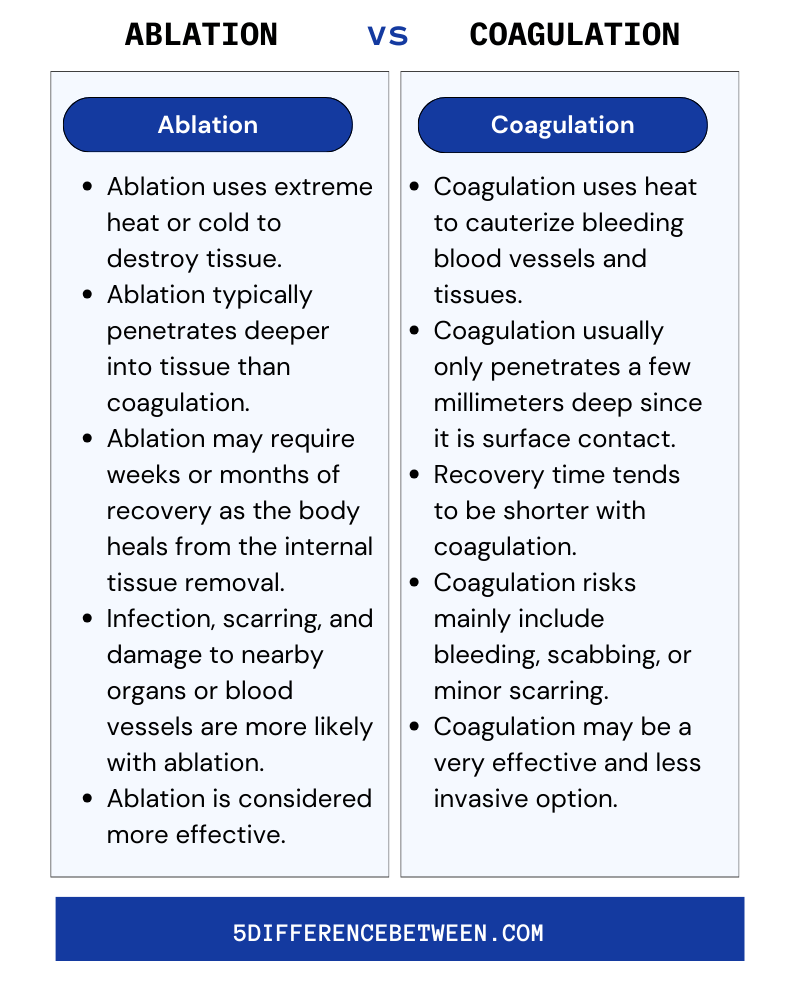
Ablation
- Ablation uses extreme heat or cold to destroy tissue.
- Ablation typically penetrates deeper into tissue than coagulation.
- Ablation may require weeks or months of recovery as the body heals from the internal tissue removal.
- Infection, scarring, and damage to nearby organs or blood vessels are more likely with ablation.
- For some conditions, Ablation is considered more effective since it destroys the underlying tissue.
Coagulation
- Coagulation uses heat to cauterize bleeding blood vessels and tissues.
- Coagulation usually only penetrates a few millimeters deep since it is surface contact.
- Recovery time tends to be shorter with coagulation since it is less invasive.
- Coagulation risks mainly include bleeding, scabbing, or minor scarring.
- For minor surface issues like bleeding or non-cancerous lesions, coagulation may be a very effective and less invasive option.
In summary, while ablation and coagulation are both used to treat medical problems, there are numerous key differences to keep in mind while determining which choice is proper in your unique circumstance. Understanding the variations in depth of remedy, effectiveness, healing time, and risks let you make the maximum informed choice with your doctor.